Basics of Finance and Trading
Financial Markets
Three financial markets deserve particular attention:
the bond market where interest rates are determined
the stock market which has a major effect on people’s wealth and on firms’ investment decisions
the foreign exchange market as fluctuations in the foreign exchange rate has major consequences for all economies.
Banks and financial institutions channel funds from people who might not put them to productive use, to people who can do so. They thus play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of the economy.
Bid Offer Spread
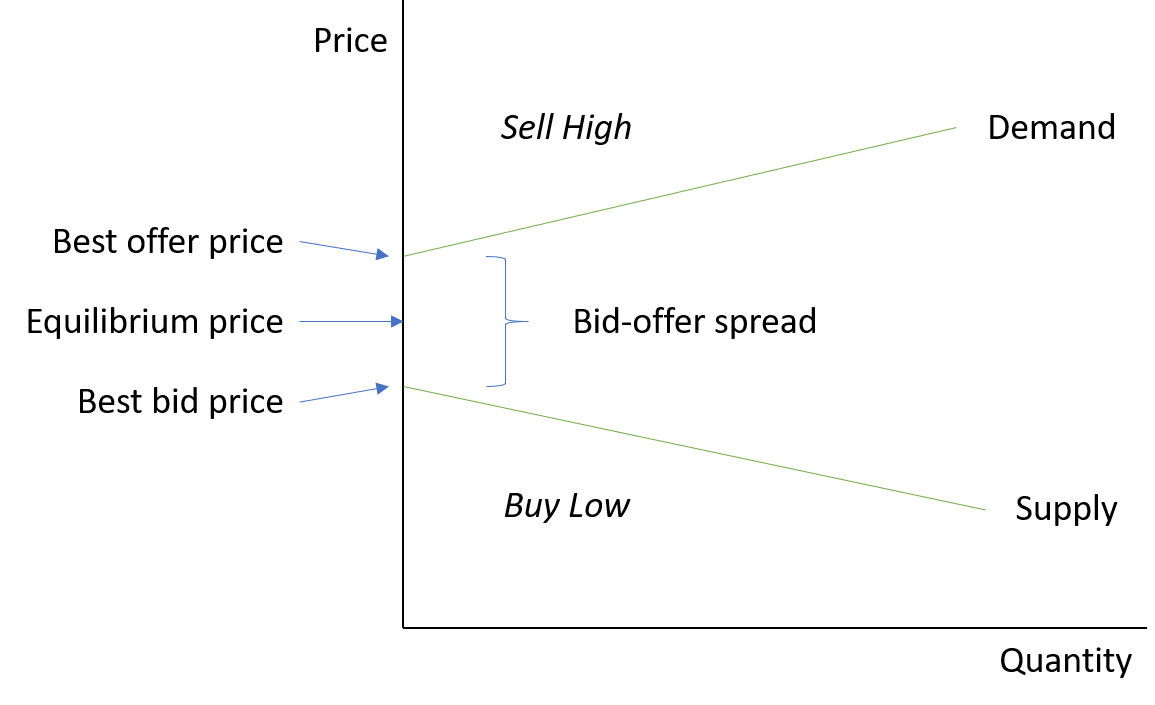
The best bid price is the maximum price you are willing to pay to buy a security.
Conversely, the best offer price is the minimum price a buyer is willing to sell you a security for.
The offer price is usually higher than the bid price because we usually buy low and sell high.
The bid offer spread is simply the difference in price between the bid and offer / ask price.
Essential Types of Financial Data
Financial data come in many shapes and forms, but can be broadly classified into:
Fundamental Data: These are publicly available data such as regulatory filings, accounting data and business analytics reported periodically. The data can include information such as assets, liabilities, sales, cost/earnings, etc.
Market Data: These include all trading activity that takes place in an exchange, such as FIX messages to fully reconstruct the trading book, or even full collections of BWIC responses.
Analytics Data: You can think of these as derived data based on the original source such as fundametal data or market data. This data is not readily available from the original source, but may be bought from investment banks and research firms with in-depth analysis. Examples include analysts recommendations, credit ratings, earnings expectations, etc.
Alternative Data: These are complementary primary data coming from government agencies, sensors, satellites, port shipments, tanker movements and pipeline traffic, that are generated along with the source data. Alternative data offers the opportunity to verify and co-relate source data, but it may be hard to process datasets that could even be non structural or non relational.
OMS and EMS Systems
The Order Management System
The OMS is the hub that structures inbound order flows and enables traders to route orders and to track trading activity and the progress of each order for various types of securities.
It is the backbone of an asset manager’s system architecture, touching on many aspects of the trading lifecycle.
It performs vital functions such as allocations, position management and communication between portfolio managers and traders. It ensures that orders are updated, reported back to the client and sent to the back-office.
The Execution Management System
The EMS is focused on real-time trading, real-time market data and analytics.
It typically offers the capability to manage orders across multiple trading venues, including exchanges, brokerage firms and alternative trading systems, sometimes with algorithmic support.
OMS-EMS Integration
OMS-EMS integration allows trades to flow seamlessly and provides automated trading using aggregated orders, orders with pending allocations, pairs, contingent orders, baskets, order programs and multiple orders from different clients for the same instrument.